The Polkadot relay chain is the core component that powers Polkadot’s vision of a fully interoperable blockchain ecosystem. Acting as the main hub, it connects multiple blockchains, known as parachains, ensuring secure data transfer, consensus, and coordination across the network. Without the relay chain, the seamless communication Polkadot offers would not be possible.
In this article, we will explore what the relay chain is, how it functions, its structure, and its real-world applications. We will also look at tools like the Polkadot relay chain explorer, diagrams explaining its architecture, and reviews from the crypto community.
Whether you’re a blockchain developer, investor, or simply curious about Polkadot’s technology, understanding the relay chain is essential to appreciating why this project stands out in the Web3 ecosystem.
Description of the Polkadot Relay Chain
The relay chain serves as Polkadot’s central blockchain, designed for speed, security, and scalability. Its primary role is not to host smart contracts or dApps directly but to coordinate parachains and manage network consensus. This separation of duties allows parachains to specialize while the relay chain ensures interoperability and data integrity.
Key responsibilities of the relay chain include:
- Maintaining network consensus through its nominated proof-of-stake (NPoS) mechanism.
- Coordinating parachain slot auctions for project onboarding.
- Facilitating cross-chain messaging using protocols like XCMP (Cross-Consensus Message Passing).
- Providing shared security to all parachains connected to it.
Key Takeaway
The Polkadot relay chain is not a typical blockchain that processes every transaction. Instead, it acts as a highly efficient coordinator, allowing connected blockchains to focus on their specific use cases while benefiting from Polkadot’s unified security and interoperability.
The relay chain acts as the central chain of data in the Polkadot network, a protocol that allows interoperability between different blockchain networks.
- The Polkadot relay chain is the central hub that enables communication and interoperability among different blockchains in the network.
- It coordinates interactions between parachains (parallel blockchains) for smooth cross-chain operations.
- Parachains run transactions in parallel rather than sequentially, resulting in faster and more efficient processing.
- Each parachain has its own validators for internal transactions, while the relay chain has its own validators for cross-parachain activities.
- The relay chain ensures all connected chains operate in sync, delegating specific functions to parachains based on their unique designs.
- All parachains share the security of the relay chain; if the relay chain rolls back, all parachains revert to maintain consistency.
- It also links to blockchain bridges, enabling asset and data transfers with external networks.
- Despite being connected, parachains can have independent rules, governance, and technical structures.
What is a Relay Chain?
In blockchain architecture, a relay chain is a central chain that connects multiple independent blockchains, enabling them to share data and assets securely. Unlike traditional blockchains that operate in isolation, a relay chain’s primary function is to manage the communication and validation processes between different blockchains.
What is the Polkadot Relay Chain?
The Polkadot relay chain is the heart of the Polkadot ecosystem. It uses a unique nominated proof-of-stake consensus, where validators, nominators, collators, and fishermen work together to maintain network security and efficiency.
Unlike Ethereum, where the main chain executes most transactions, Polkadot’s relay chain is optimized for coordination. Parachains handle their own execution while relying on the relay chain for final settlement and security.
Polkadot Hosting dApps via the Relay Chain
While the relay chain itself does not directly host decentralized applications, it enables parachains to do so efficiently. For example, a parachain focused on DeFi can run complex smart contracts while using the relay chain for secure cross-chain asset transfers.
This design makes Polkadot attractive for developers building on Web3 since they can focus on innovation without worrying about building their own security framework. You can explore how other projects approach blockchain integration in our guide to Chainlink Labs Careers and decentralized oracle solutions.
Polkadot Relay Chain Explorer
The relay chain explorer is a tool that provides real-time data about the Polkadot network. Users can monitor:
- Validator performance and staking details.
- Parachain slot auctions and winners.
- Cross-chain transactions and block finalization times.
This transparency builds trust among investors and developers while providing essential metrics for network optimization.
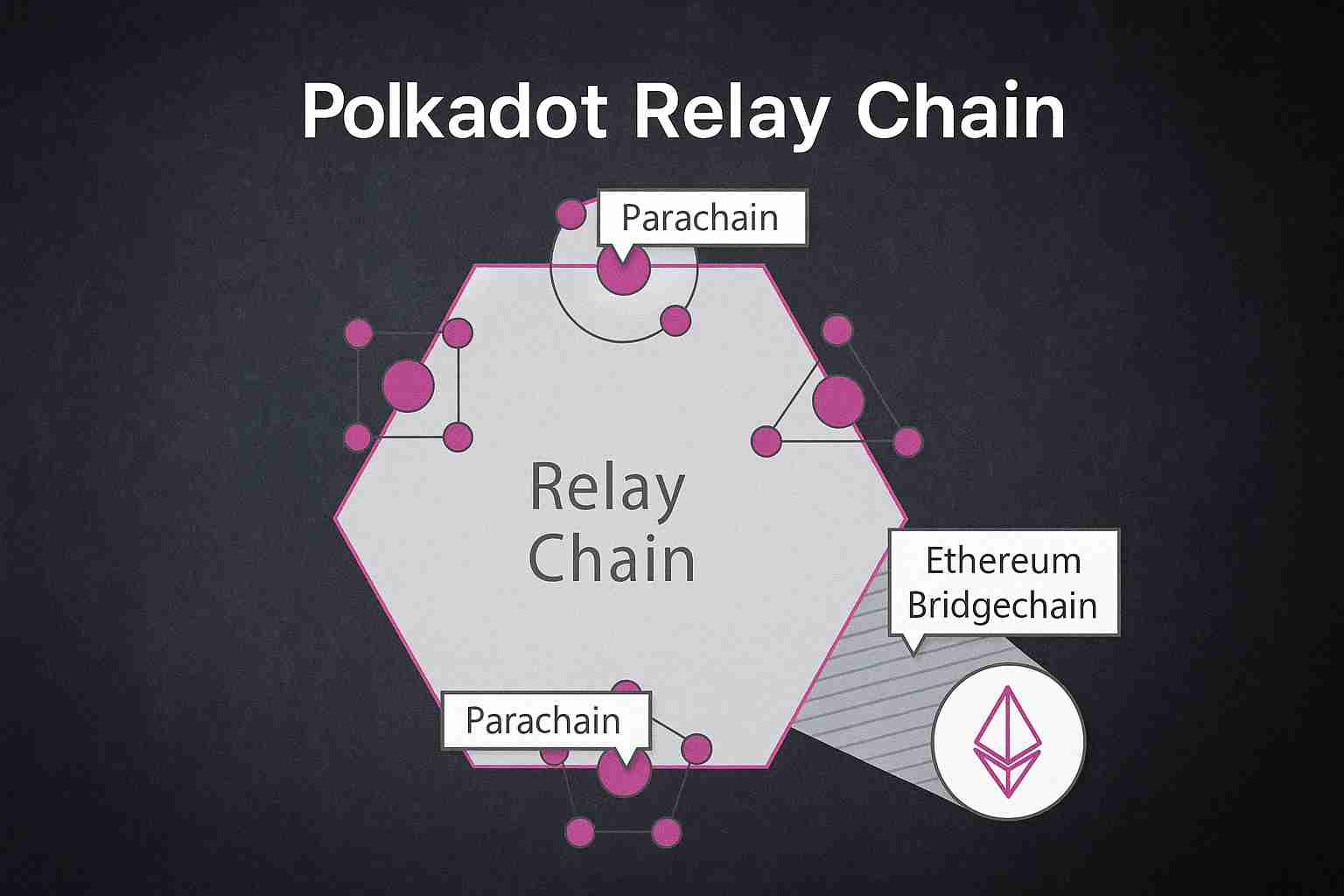
Polkadot Relay Chain Diagram
A relay chain diagram visually explains how Polkadot’s architecture works. At the center is the relay chain, surrounded by parachains, each connected through validators. Bridges extend the ecosystem to external blockchains like Ethereum and Bitcoin.
Polkadot Relay Chain Review
The relay chain has received praise for its innovative approach to scalability and interoperability. Reviewers highlight:
- Pros: High throughput, shared security, flexible parachain design.
- Cons: Complexity for new developers, limited direct smart contract hosting.
If you are exploring other high-potential blockchain projects, check out our analysis of Next 10x Crypto Projects to see how Polkadot compares.
Polkadot: What Layer is It?
Polkadot operates as a Layer 0 blockchain. This means it serves as the foundational network upon which Layer 1 blockchains (parachains) are built. The relay chain is the Layer 0 element that ties all these Layer 1 blockchains together, enabling them to communicate and share security.
Polkadot Portal
The Polkadot Portal is the official interface for interacting with the Polkadot network. From here, users can manage staking, participate in governance, view parachain auctions, and monitor relay chain performance.
Polkadot Relay Chain Structure
The relay chain structure consists of:
- Validators – Secure the network and validate parachain blocks.
- Nominators – Support validators by staking DOT tokens.
- Collators – Produce blocks for parachains and submit them to validators.
- Fishermen – Detect malicious activity and report it.
This structure ensures efficiency and security while maintaining decentralization.
Polkadot Relay Chain Auction
Parachains are onboarded through slot auctions. Projects bid DOT tokens for the right to connect to the relay chain. The highest bidders secure a slot for a set period, allowing them to leverage Polkadot’s shared security. For insights into similar blockchain project launches, explore our guide on Best IDO Launchpad 2025.
Conclusion
The Polkadot relay chain is a groundbreaking innovation in blockchain interoperability. By acting as a Layer 0 network, it provides scalability, shared security, and seamless cross-chain communication. For developers, it’s an infrastructure that reduces barriers to building robust blockchain solutions. For investors, it represents a long-term play in the multi-chain future of Web3.
Summary
- Polkadot relay chain is the central hub for Polkadot’s blockchain ecosystem.
- It connects parachains, enables cross-chain transactions, and ensures shared security.
- Acts as a Layer 0 network powering scalable, interoperable blockchain solutions.
FAQs
1. What is the Polkadot relay chain?
It’s the central blockchain that coordinates and secures all parachains in the Polkadot ecosystem.
2. Does the relay chain host dApps?
No, but it enables parachains to host dApps securely and efficiently.
3. How does the relay chain achieve interoperability?
Through protocols like XCMP for cross-chain message passing.
4. What consensus does the relay chain use?
Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS).
5. Can I view relay chain activity?
Yes, through the Polkadot relay chain explorer.
6. Is Polkadot a Layer 1 or Layer 0 blockchain?
It’s a Layer 0 blockchain connecting multiple Layer 1 parachains.
7. How are parachains connected to the relay chain?
Through parachain slot auctions.
8. What are the benefits of the relay chain?
Shared security, scalability, and cross-chain interoperability.
9. Where can I learn more about Polkadot projects?
You can explore our 10 Top Polkadot Parachains.
10. Why is the relay chain important for Web3?
It enables a decentralized, multi-chain internet by connecting diverse blockchains.
11. What is relay chain of polkadot” The relay chain acts as the central chain of data in the Polkadot network, a protocol that allows interoperability between different blockchain networks.